

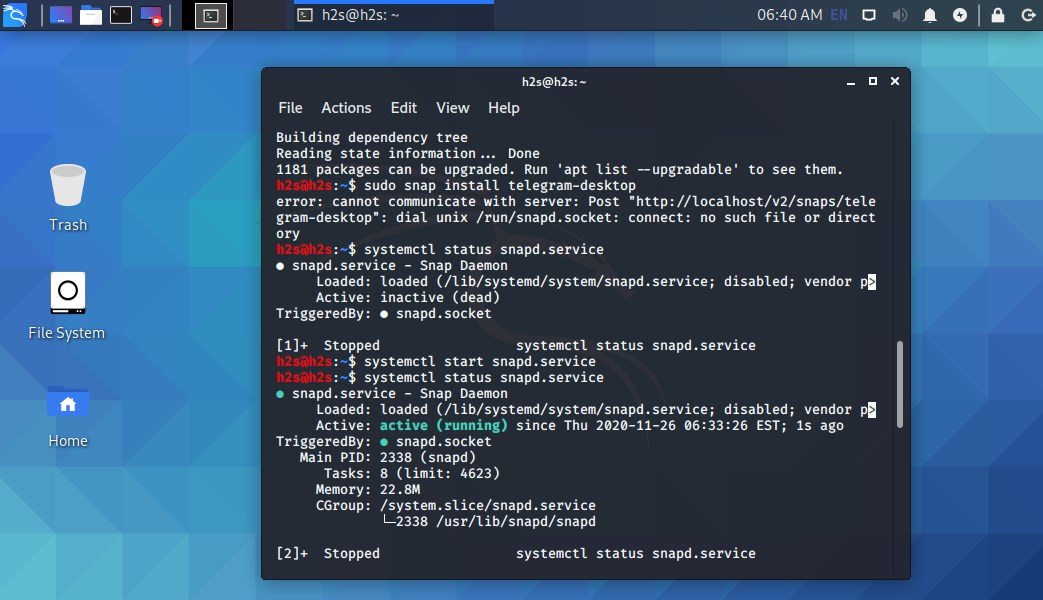
Thus, a signed 32-bit integer can only represent integer values from −(2 31) to 2 31 − 1 inclusive. Unix time has historically been encoded as a signed 32-bit integer, a data type composed of 32 binary digits (bits) which represent an integer value, with 'signed' meaning that one bit is reserved to indicate sign (+/–). Unix time is defined as the number of seconds elapsed since 00:00:00 UTC on 1 January 1970 (an arbitrarily chosen time), which has been dubbed the Unix epoch. Many computer systems measure time and date as Unix time, an international standard for digital timekeeping. There is no universal solution to the problem, though many modern systems have been upgraded to measure Unix time with signed 64-bit integers which will not overflow for 292 billion years – which is, precisely, after 15:30:07 on 4 December 292277026596. The most vulnerable systems are those which are infrequently or never updated, such as legacy and embedded systems. Some applications that use future dates have already encountered the bug. The problem is similar in nature to the Year 2000 problem.Ĭomputer systems that use time for critical computations may encounter fatal errors if the Y2038 problem is not addressed. Attempting to increment to the following second (03:14:08) will cause the integer to overflow, setting its value to −(2 31) which systems will interpret as 2 31 seconds before epoch (20:45:52 UTC on 13 December 1901). The data type is only capable of representing integers between −(2 31) and 2 31 − 1, meaning the latest time that can be properly encoded is 2 31 − 1 seconds after epoch (03:14:07 UTC on 19 January 2038). The problem exists in systems which measure Unix time – the number of seconds elapsed since the Unix epoch (00:00:00 UTC on 1 January 1970) – and store it in a signed 32-bit integer. The Year 2038 problem (also known as Y2038, Y2K38, the Epochalypse, or the Friday 13th Bug ) is a time formatting bug in computer systems with representing times after 03:14:07 UTC on 19 January 2038. The overflow error will occur at 03:14:08 on 19 January 2038. In a previous version of himself he wrote books on technology.Ĭontent is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-SA 4.An animated visual of the bug in action. He is interested in people, music, food and writing. You can edit it here and send me a pull request.

#UNIX ERROR SEAIQ UPDATE#
Have an update or suggestion for this article?

Linux and Unix tee command help and examples.echo 'foo' > fileĪs part of a pipe tee can take the input, elevate permissions and write to the file. Trying to append to this file as a normal user results in a permissions error. To write to a privileged file tee may be used as part of a pipe to elevate to sudo permissions.
#UNIX ERROR SEAIQ HOW TO#
How to write to a privileged file using tee
tail -f /var/log/nginx/access.log | grep -line-buffered "HTTP/2.0" | tee -a http2.log Using tee the live logs can be streamed to standard output and also write to a file for further analysis later. In this example there is a requirement to analyse the HTTP2 traffic going through an nginx server. How to watch log files and write to a file ls ~/ | tee pipe1.txt | grep ^b | tee pipe2.txt | sort -r This can be for debugging purposes or to take a backup. cat foo.txtĪs data flows through UNIX pipelines it can be useful to take a snapshot of the state of the data. To use tee and append to a file rather use the -a option. This writes the output of the first command to standard output and to a file called foo.txt How to write to a file and append output To write to standard output and a file use tee after a pipe and specify the file or files to write to. How to write to standard output and a file The command is named after T splitter used in plumbing. It supports writing whatever it is given from standard input to standard output and optional writing to one or more files. The tee command in UNIX is a command line utility for copying standard input to standard output. How to write to a privileged file using tee.How to watch log files and write to a file.How to write to a file and append output.How to write to standard output and a file.Examples of writing to a file, appending to a file and writing to a privileged file.Įstimated reading time: 2 minutes Table of contents Last updated Saturday, Linux and Unix tee command tutorial with examples Tutorial on using tee, a UNIX and Linux command for copying standard input to standard output and making a copy to one or more files. Linux and Unix tee command tutorial with examples | George Ornbo


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
